dbPEX – PEX-genendatabase
Missie
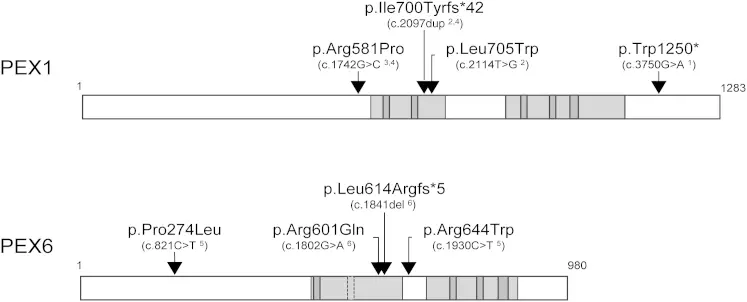
Door genetische variaties te catalogiseren die betrokken zijn bij peroxisomale assemblageziekten, hopen we de analyse van deze variaties te versnellen en hun rol in gezondheid en ziekte beter te begrijpen.

dbPEX-beleid
Disclaimer
dbPEX is niet bedoeld voor klinisch gebruik, waaronder diagnose, genetische counseling of behandeling van een gezondheidsprobleem of ziekte. dbPEX verstrekt ook geen medisch advies en raadt gebruikers aan om gekwalificeerde professionals te raadplegen voor diagnose, genetische counseling of behandeling van gezondheidsproblemen of ziekten, of voor antwoorden op persoonlijke vragen.
Aansprakelijkheid
dbPEX betracht alle redelijke zorg om ervoor te zorgen dat de database en de daarin opgenomen gegevens van hoge kwaliteit zijn; het geeft echter geen garantie, expliciet of impliciet, met betrekking tot de juistheid of volledigheid daarvan, noch dat deze database of de daarin opgenomen gegevens geschikt zijn voor een bepaald doel, zoals diagnose, genetische counseling of behandeling van patiënten. dbPEX aanvaardt geen aansprakelijkheid voor gevolgen die voortvloeien uit eventuele onjuistheden, weglatingen of verkeerd gebruik van de informatie.
Laten we contact maken
Kom in contact met je klanten om ze betere service te bieden. Je kunt de formuliervelden aanpassen om preciezere informatie te verzamelen.